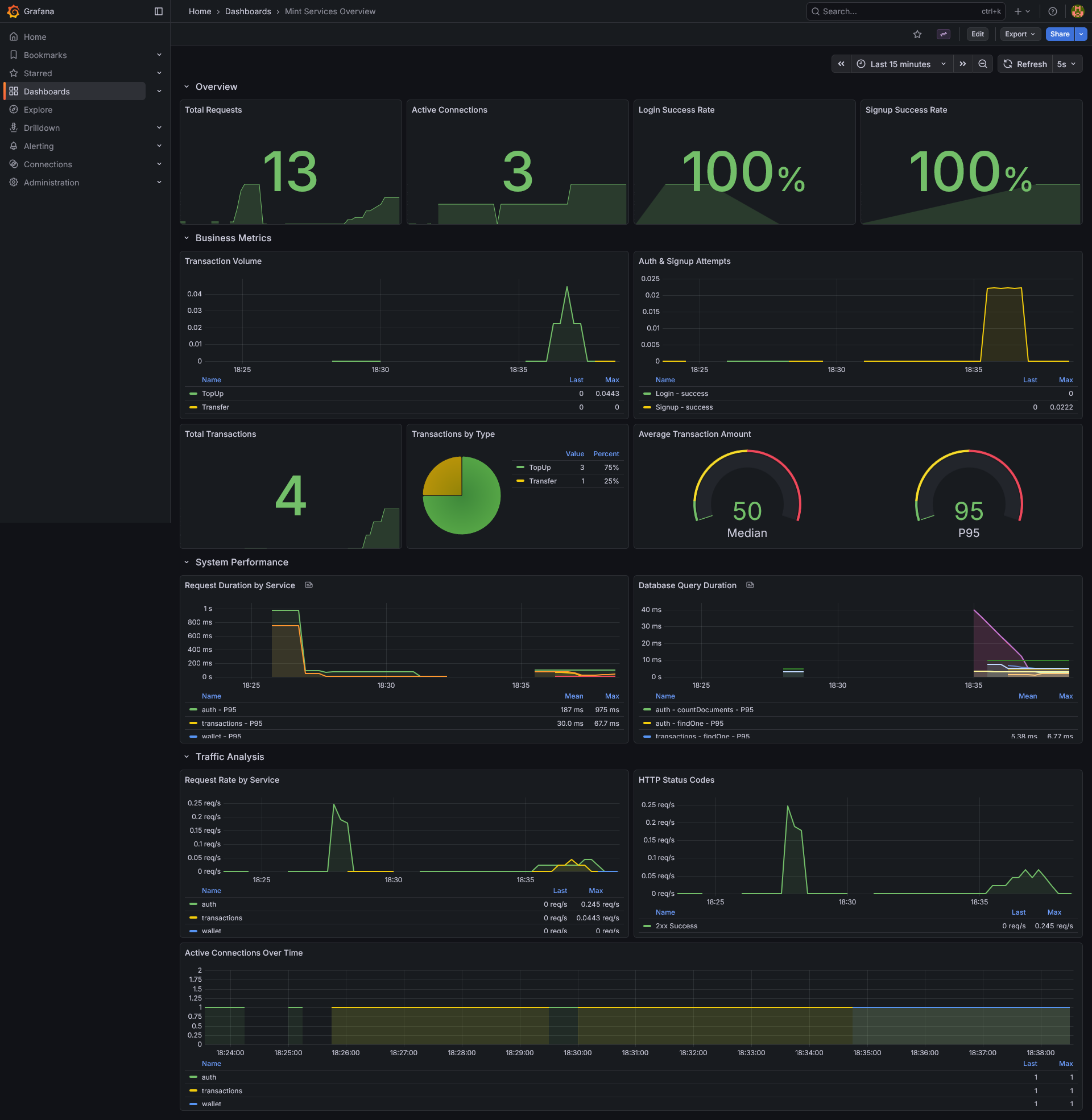
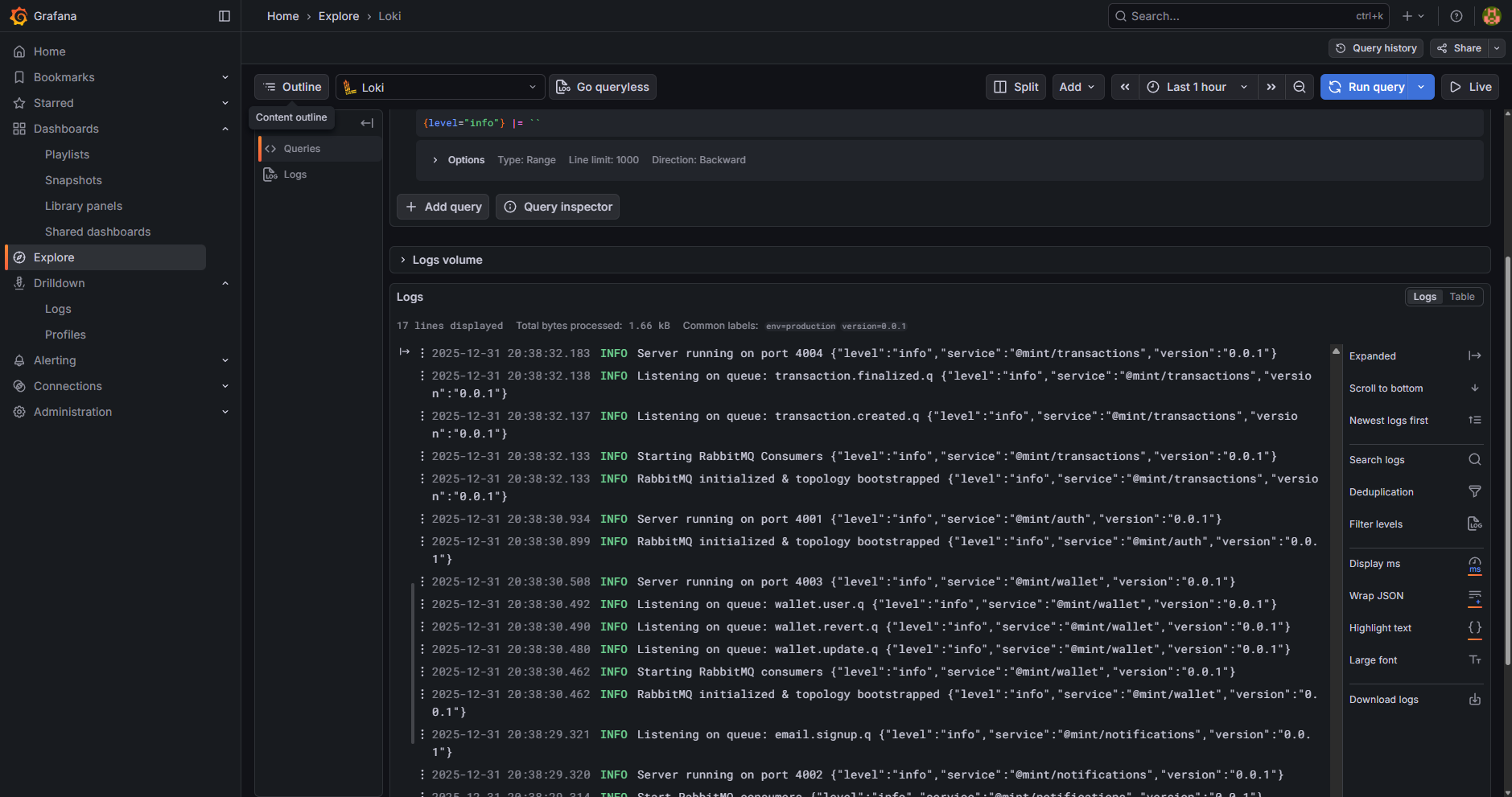
Mint demonstrates modern architectural patterns including JWT authentication, distributed transactions, message queuing, and API gateway design.
Overview
Mint is a production-grade microservices wallet system designed to handle real-world financial transactions with reliability and scalability. The system showcases best practices in distributed systems architecture, including event-driven communication, service isolation, and comprehensive observability.
Key Features
Security
- JWT (RS256) with JWKS - Industry-standard token authentication with key rotation support
- Argon2 Password Hashing - Memory-hard hashing algorithm resistant to GPU attacks
- HTTP-only Cookies - Secure token storage preventing XSS attacks
Wallet Operations
- Event-Driven Creation - Wallets are created asynchronously upon user registration
- Real-Time Balance Updates - Immediate reflection of transactions
- Complete Transaction History - Audit trail for all operations
Transaction Processing
- State Machine - Transactions flow through PENDING → PROCESSING → COMPLETED/FAILED
- Top-ups and Transfers - Support for both inbound and peer-to-peer transfers
- Idempotency - Safe retry handling for failed operations
Smart Notifications
- Automated Email Alerts - Signup confirmations and transaction receipts
- RabbitMQ Integration - Reliable message delivery with retry logic
- Template System - Customizable notification templates
Performance & Caching
- Redis Caching - 80-90% cache hit rates for frequently accessed data
- Connection Pooling - Efficient database connection management
- Query Optimization - Indexed queries for fast lookups
Observability
- Prometheus Metrics - Custom metrics for business and technical KPIs
- Grafana Dashboards - Real-time visualization of system health
- Loki Log Aggregation - Centralized logging with search capabilities
- Distributed Tracing - Request correlation across services
Testing
- 112 Comprehensive Tests - Unit, integration, and consumer contract tests
- MongoDB Memory Server - Fast, isolated database testing
- Supertest - HTTP assertion library for API testing
Architecture
The system follows a microservices architecture with four independent services communicating asynchronously through RabbitMQ:
flowchart TB
subgraph Client
A[Web/Mobile App]
end
subgraph Gateway
B[NGINX API Gateway]
end
subgraph Services
C[Auth Service
:4001]
D[Wallet Service
:4003]
E[Transactions Service
:4004]
F[Notifications Service
:4002]
end
subgraph MessageBroker
G[(RabbitMQ)]
end
subgraph DataStores
H[(MongoDB
Auth DB)]
I[(MongoDB
Wallet DB)]
J[(MongoDB
Txn DB)]
K[(Redis
Cache)]
end
subgraph Observability
L[Prometheus]
M[Grafana]
N[Loki]
end
A --> B
B --> C
B --> D
B --> E
C --> H
C --> K
C -.->|events| G
D --> I
D --> K
G -.->|consume| D
E --> J
E -.->|events| G
G -.->|consume| E
G -.->|consume| F
C --> L
D --> L
E --> L
F --> L
L --> M
N --> M
Service Responsibilities
| Service | Port | Responsibility |
|---|---|---|
| Auth | 4001 | User authentication, JWT management, session handling |
| Wallet | 4003 | Balance management, wallet creation, event consumption |
| Transactions | 4004 | Payment processing, transfers, state management |
| Notifications | 4002 | Email delivery, notification templates, event handlers |
Design Principles
- Database per Service - Each service owns its data, ensuring loose coupling
- Event Sourcing - Critical operations publish events for audit and replay
- API Gateway - NGINX handles routing, rate limiting, and load balancing
- Circuit Breaker - Graceful degradation when downstream services fail
Getting Started
# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/sreekarnv/mint.git
cd mint
# Start all services with Docker
docker-compose up -d
# Access the services
# API Gateway: http://localhost:8080
# RabbitMQ Management: http://localhost:15672
# Grafana: http://localhost:3000
# Prometheus: http://localhost:9090What I Learned
Building Mint taught me valuable lessons in distributed systems:
- Event-driven architecture requires careful consideration of eventual consistency
- Observability is not optional - you can’t fix what you can’t see
- Testing microservices requires a different approach than monoliths
- Docker Compose is powerful for local development but has limitations at scale